Nursing Goal For Ineffective Breathing Pattern
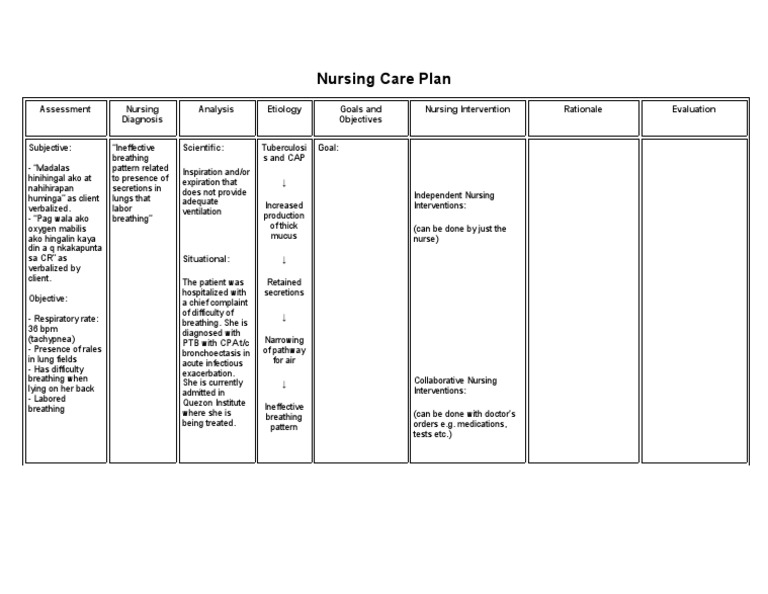
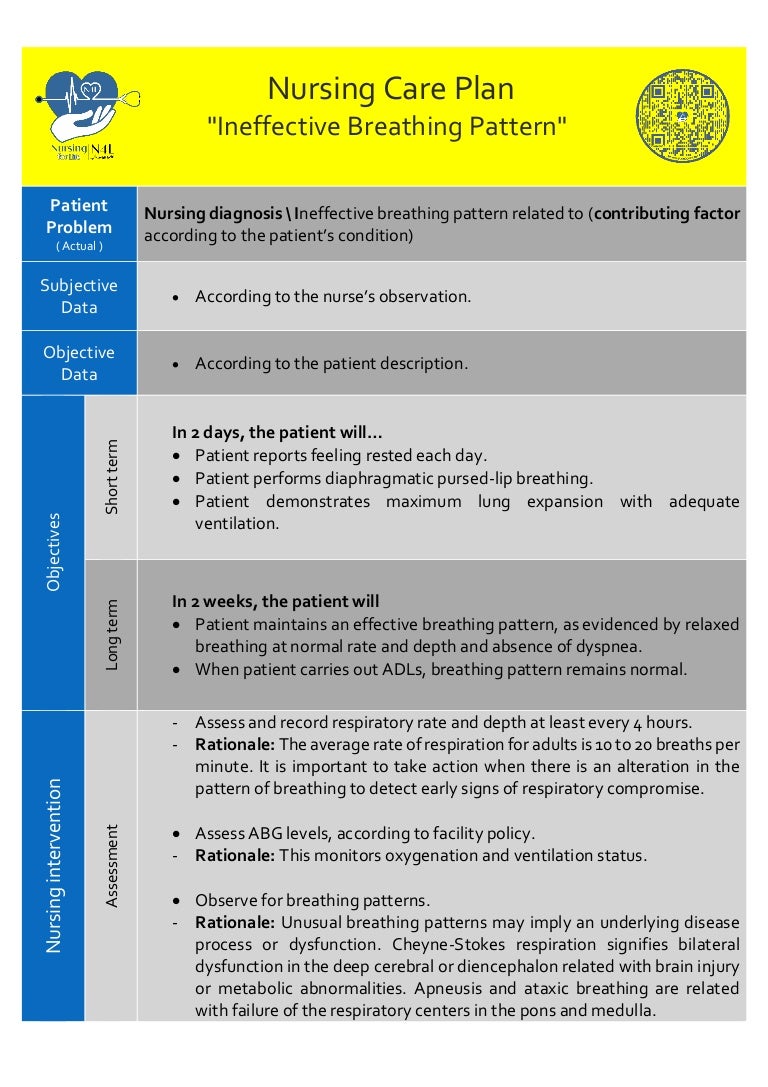
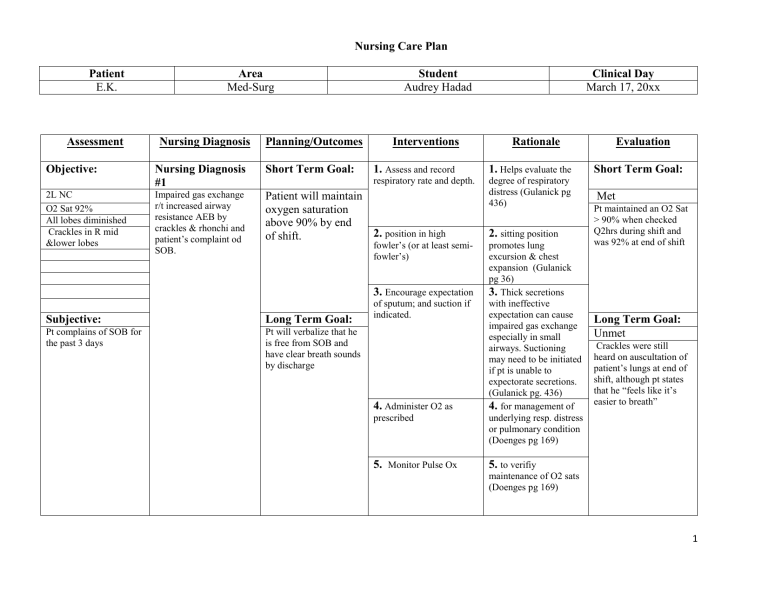
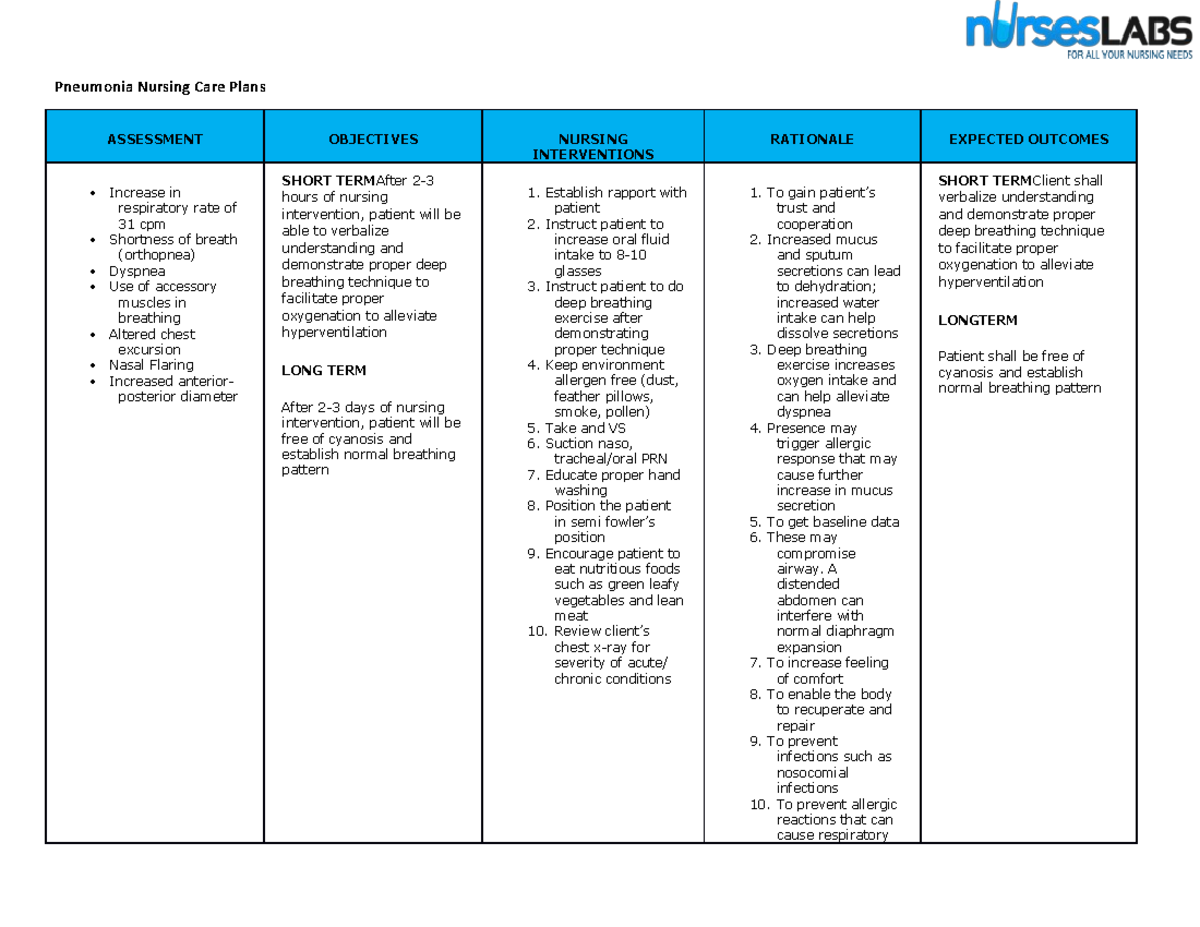
Nursing Goal For Ineffective Breathing Pattern - It is important to take action when respirations exceed 30 breaths per minute. When lung tissues are injured, the alveoli become permeable to large molecules, allowing more proteins, debris, and fluids to enter lungs. Web ineffective breathing patterns can happen in various situations, but they are always dangerous for patients’ health. Web the following are common nursing care planning goals and expected outcomes for ineffective airway clearance: Patient’s o saturation level has risen to a normal rate greater than or equal to 95% by end of shift. The goal of treatment for patients with bronchitis is to relieve symptoms and prevent complications like pneumonia. Pneumothorax or collapsed lung is caused by air leaking into the pleural cavity. In a normal lung, negative pressure exists between the visceral and parietal pleura or the pleural space. Web during the nurse’s first assessment and each daily assessment, the following needs to be documented: The disease process of ards is broken down into three stages: Web irregular breathing (hyperventilating), nasal flaring, mouth breathing, gasping for air, and use of accessory muscles are symptoms of an ineffective breathing pattern that require immediate attention. Give your recommendations for changing the care plan to Web during the nurse’s first assessment and each daily assessment, the following needs to be documented: This nursing care plan and diagnosis is for the following condition: When the breathing pattern is ineffective, the body will likely not get enough oxygen in the cells. Pneumothorax or collapsed lung is caused by air leaking into the pleural cavity. Include evidenced based rationales for each nursing intervention using your textbooks. Web improved breathing pattern: Discuss the role of the nurse in the management of ards. Web auscultate breath sounds at least every 4 hours to detect decreased or adventitious breath sounds; Include evidenced based rationales for each nursing intervention using your textbooks. Web the following are common nursing care planning goals and expected outcomes for an ineffective breathing pattern: State whether or not the goal was met. Web ineffective breathing pattern. Maegan wagner, bsn, rn, ccm. Patient demonstrates a baseline respiratory rate,. The average rate of respiration for adults is 10 to 20 breaths per minute. Web ineffective breathing pattern. When the breathing pattern is ineffective, the body will likely not get enough oxygen in the cells. This nursing diagnosis is appropriate for patients who cannot maintain adequate oxygenation resulting in insufficient tissue perfusion and carbon. Patient will maintain an effective breathing pattern with normal respiratory rate, depth, and oxygen saturation. Patient will deny shortness of breath. In a normal lung, negative pressure exists between the visceral and parietal pleura or the pleural space. Web ineffective breathing patterns can happen in various situations, but they are always dangerous for patients’ health. Patient’s o saturation level has. This includes reducing the respiratory rate, promoting deep and efficient breaths, and minimizing the use of accessory muscles for breathing. The aim is to help the patient achieve a regular, effective breathing pattern. When lung tissues are injured, the alveoli become permeable to large molecules, allowing more proteins, debris, and fluids to enter lungs. This nursing diagnosis is appropriate for. Web the short term goals are for the patient to understand their treatment and demonstrate proper breathing techniques to alleviate symptoms. Nurses take the lead in providing supportive interventions and. In a normal lung, negative pressure exists between the visceral and parietal pleura or the pleural space. Patient’s o saturation level has risen to a normal rate greater than or. Web irregular breathing (hyperventilating), nasal flaring, mouth breathing, gasping for air, and use of accessory muscles are symptoms of an ineffective breathing pattern that require immediate attention. Nurses take the lead in providing supportive interventions and. Patient will maintain an effective breathing pattern with normal respiratory rate, depth, and oxygen saturation. Give your recommendations for changing the care plan to. Web ineffective breathing pattern nursing diagnosis & care plan. To identify the predicting factors and sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative related value of nursing diagnosis ineffective breathing pattern among patients of an intensive care unit. Ineffective breathing pattern, dyspnea, respiratory distress syndrome, hyoxia, acute respiratory failure, hypoxemia, and respiratory illness. It is important to take action when respirations exceed 30. Distinguish normal and abnormal assessment data. Web during the nurse’s first assessment and each daily assessment, the following needs to be documented: Nursing diagnoses, care plans, assessment & interventions. When the breathing pattern is ineffective, the body will likely not get enough oxygen in the cells. Patient demonstrates a baseline respiratory rate,. When lung tissues are injured, the alveoli become permeable to large molecules, allowing more proteins, debris, and fluids to enter lungs. Nursing diagnoses, care plans, assessment & interventions. Monitor respiratory rate, ease of breathing, and depth of respiration. Web during the nurse’s first assessment and each daily assessment, the following needs to be documented: The disease process of ards is. This includes reducing the respiratory rate, promoting deep and efficient breaths, and minimizing the use of accessory muscles for breathing. As a medical professional, you will provide nursing interventions to help alleviate the ineffective airway clearance and improve the overall function of the respiratory system. The aim is to help the patient achieve a regular, effective breathing pattern. Patient will. Maegan wagner, bsn, rn, ccm. Web the following are common nursing care planning goals and expected outcomes for an ineffective breathing pattern: The disease process of ards is broken down into three stages: Patient will maintain a patent airway as evidenced by clear breath sounds, oxygen saturation within normal limits, and the ability to cough to clear secretions. This template is particularly crucial for treating individuals with respiratory issues like copd, asthma, or those experiencing pain affecting their breathing. Distinguish normal and abnormal assessment data. Web ineffective breathing pattern. Assess the patient for objective and subjective manifestations of impaired oxygenation. The long term goals are for the patient to be free of cyanosis and establish normal breathing. How can nurses help a patient with an ineffective breathing pattern? Give your recommendations for changing the care plan to Patient demonstrates a baseline respiratory rate,. Web ineffective breathing pattern nursing diagnosis & care plan. Include evidenced based rationales for each nursing intervention using your textbooks. The average rate of respiration for adults is 10 to 20 breaths per minute. The goal of treatment for patients with bronchitis is to relieve symptoms and prevent complications like pneumonia.SOLUTION Nursing care plan ineffective breathing pattern related to
SOLUTION Nursing care plan ineffective breathing pattern poliomyelitis
Nursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern) Anxiety Applied
Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Ineffective Breathing Pattern Nursing Care Plan
Ineffective Breathing Pattern Nursing Care Plan
NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern Tala
Ineffective Breathing Pattern Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern
117006719 Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan
Web Ineffective Breathing Patterns Can Happen In Various Situations, But They Are Always Dangerous For Patients’ Health.
When The Breathing Pattern Is Ineffective, The Body Will Likely Not Get Enough Oxygen In The Cells.
Interpret Diagnostic Tests And Lab Values Indicative Of A Disturbance In Oxygenation.
Web The Following Are Common Nursing Care Planning Goals And Expected Outcomes For Ineffective Airway Clearance:
Related Post: