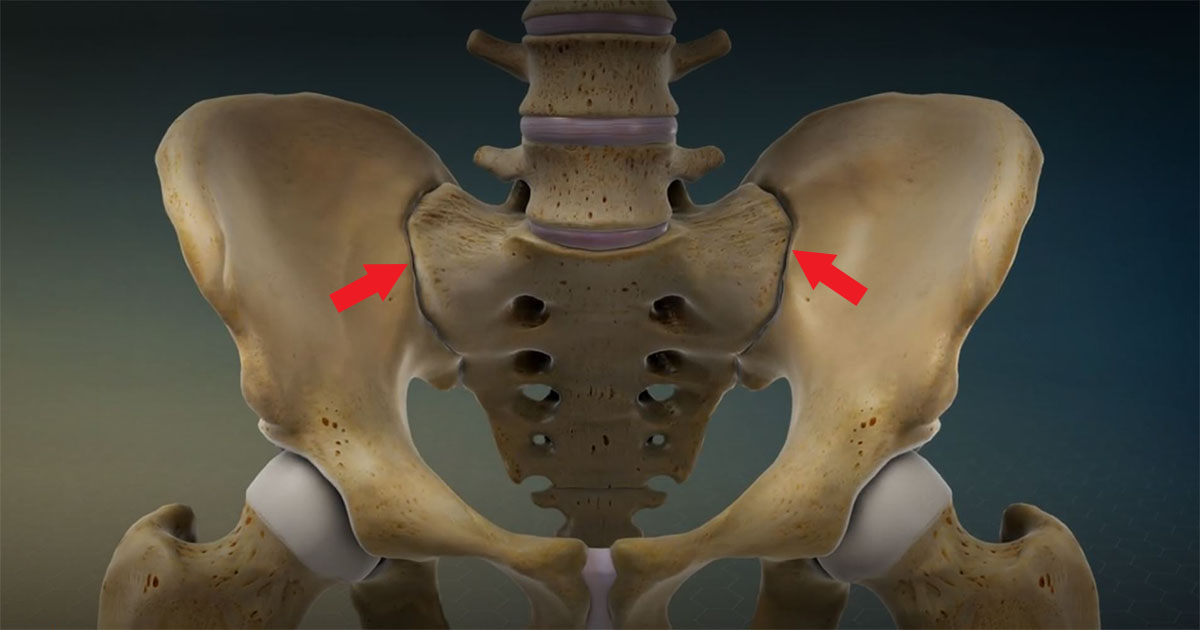
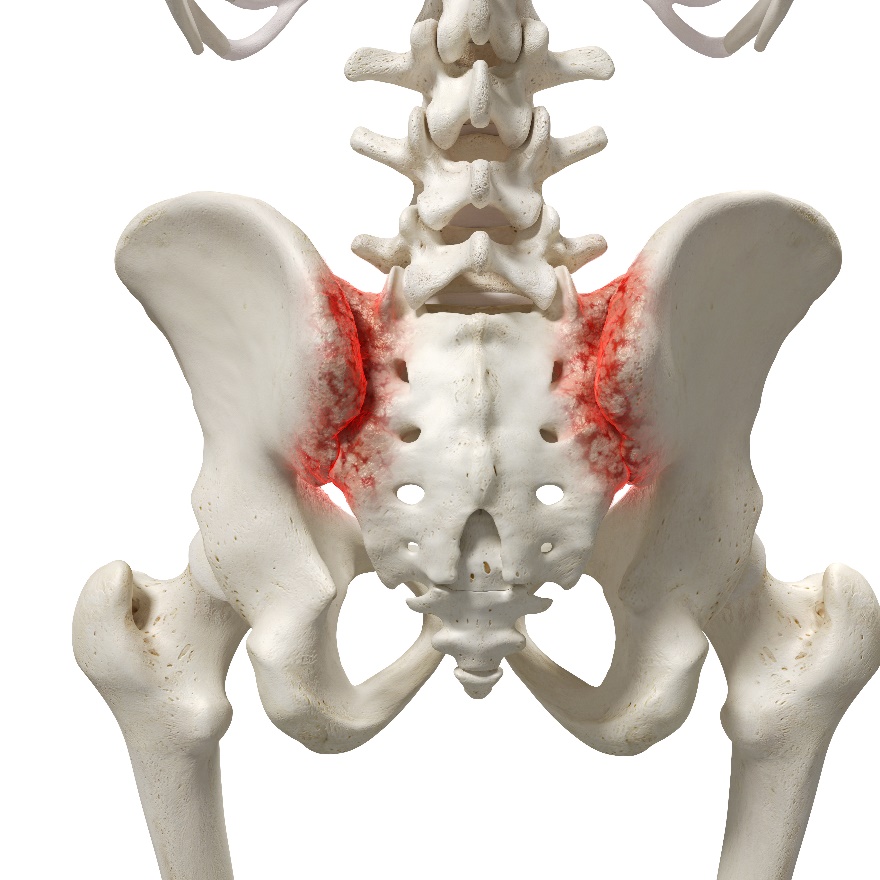
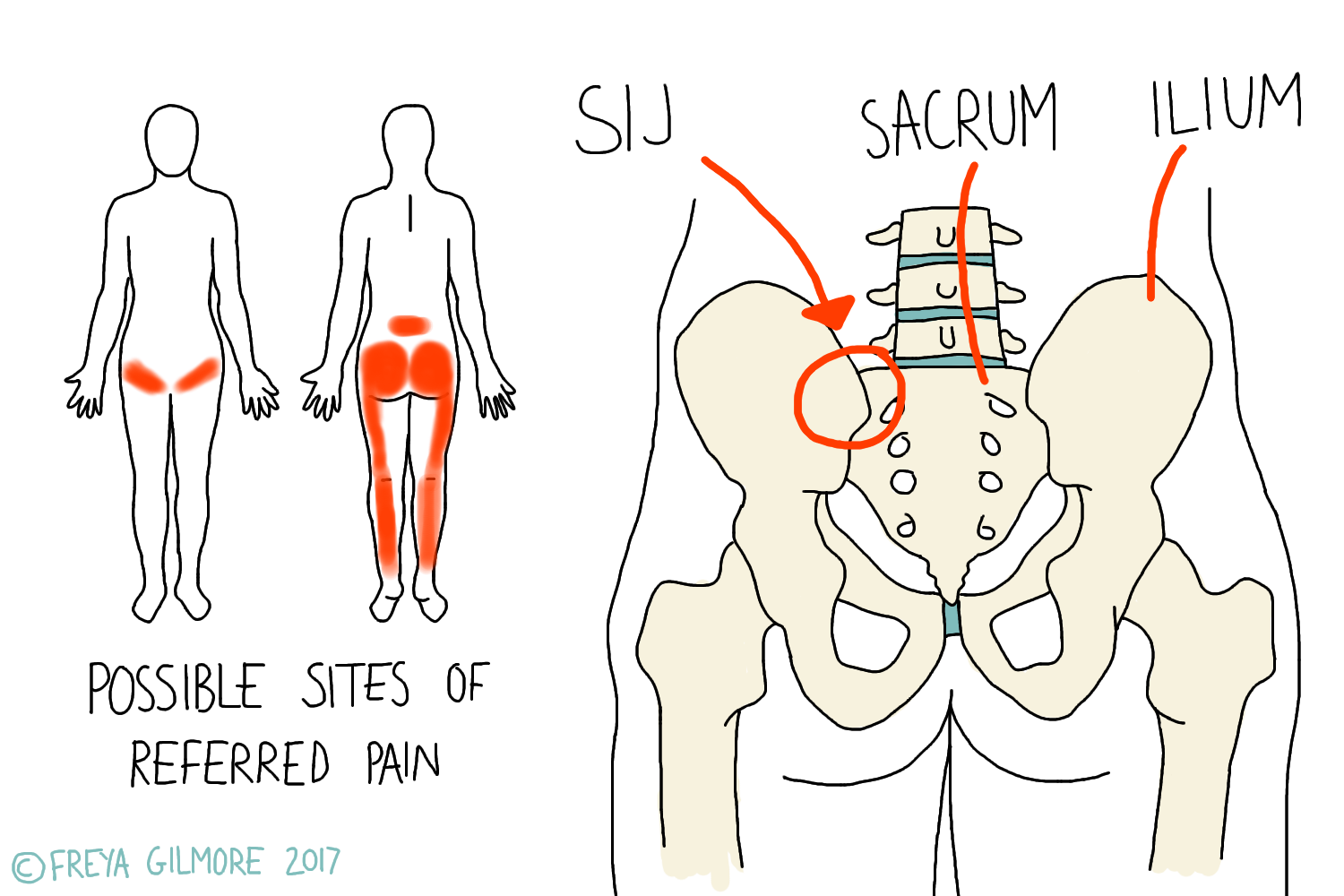
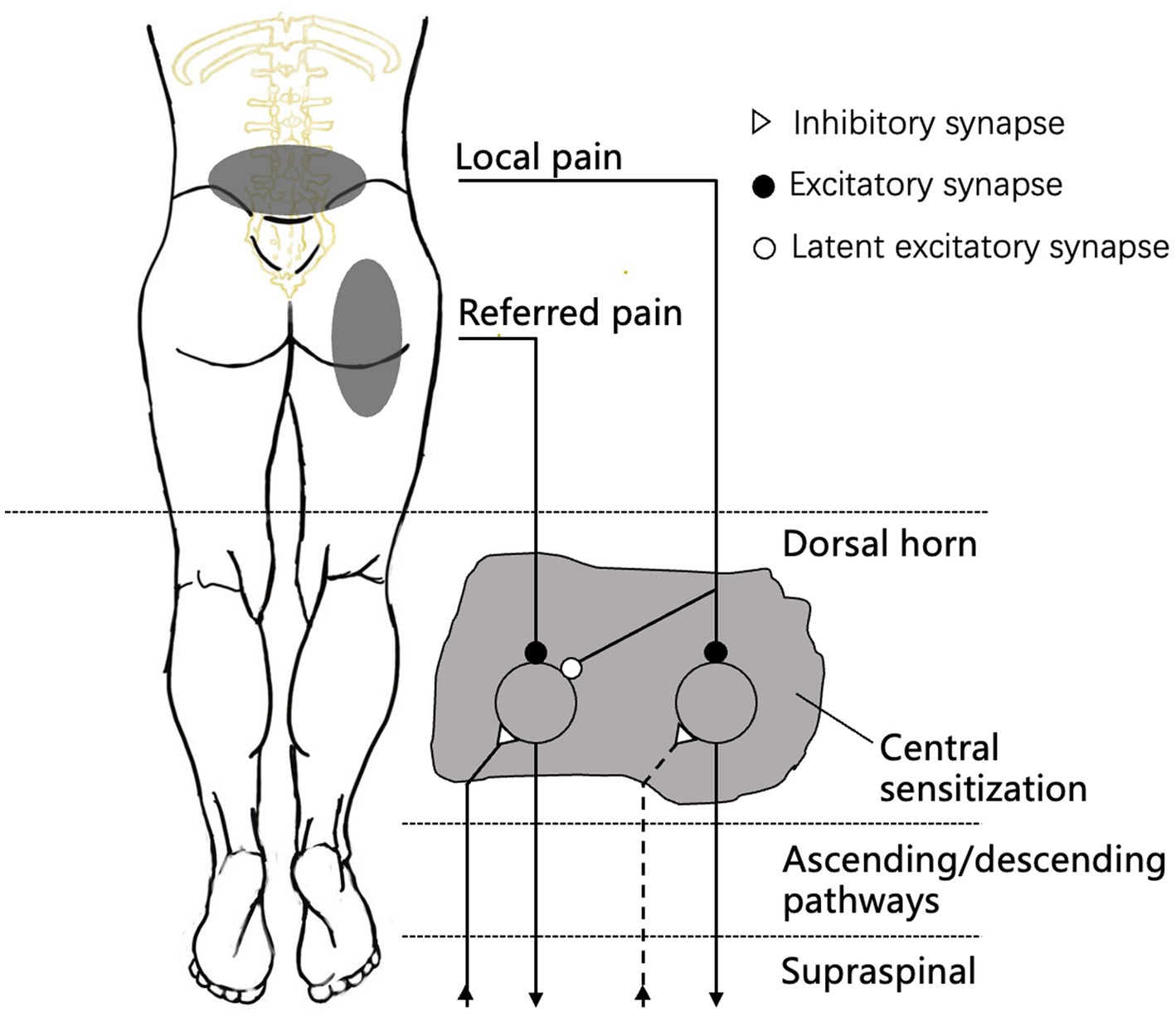
Sacroiliac Joint Referral Pattern
Sacroiliac Joint Referral Pattern - Using a pain diagram to map out the location of the pain is often very helpful in diagnosis. However, all of these diagnostic tools have limitations. If numbness and tingling or weakness is present, an alternative diagnosis should be considered. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a term used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint (si joint). A complete history and physical examination are critical in diferentiating other. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Identify the etiology of sacroiliac joint injury medical conditions and emergencies. Sacroiliac joint syndrome is a significant source of pain in 15% to 30% of people with mechanical low back pain. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. Diagnosis can be aided by pain referral patterns, historical features, physical examination maneuvers, and imaging. All 10 individuals experienced discomfort upon initial injection, with the most significant sensation felt directly around the injection site. Sij dysfunction generally refers to aberrant position or movement of sij structures that may or may not result in pain. Web proposed criteria for diagnosis of sacroiliac joint dysfunction can include pain in the area of the sacroiliac joint, reproducible pain with provocative maneuvers, and pain relief with a local anesthetic injection into the sij. Pain is the main symptom of si joint dysfunction. Web referral patterns are important to understand in accurately diagnosing and treating sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Review the appropriate evaluation of sacroiliac joint injury. Identify the etiology of sacroiliac joint injury medical conditions and emergencies. Accurate diagnosis of sacroiliac joint (sij) pain is challenging. The constellation of symptoms attributed to sijs includes pain referral to numerous anatomic regions. If numbness and tingling or weakness is present, an alternative diagnosis should be considered. Web the variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying locations of injury with the sacroiliac joint. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. Web medicare and medicaid. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with. Nevertheless, there is considerable overlap in referral areas, although the pain has been irradiated from various spinal elements ( 54 ). Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the buttocks or lower back, and the. Web sacroiliac joint (sij) pain refers. Accurate diagnosis of sacroiliac joint (sij) pain is challenging. Web the variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying locations of injury with the sacroiliac joint. However, all of these diagnostic tools have limitations. The constellation of symptoms attributed to sijs includes pain. Sij dysfunction generally refers to aberrant position or movement of sij structures that may or may not result in pain. All 10 individuals experienced discomfort upon initial injection, with the most significant sensation felt directly around the injection site. This pain may worsen with prolonged sitting or standing and can resemble symptoms of sciatica. Hospital outpatient prospective payment and ambulatory. A complete history and physical examination are critical in diferentiating other. Radiation to the groin or fortin area also suggest sacroiliac joint as a source. Symptoms that suggest that the sacroiliac joint (sij), as opposed to pathology of the lumbar spine or hip, may be a source of pain include pain with position changes, such as standing from a seated. It can cause sharp, stabbing pain that starts in the hips and pelvis and radiates into the lower back and down the thighs. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Diagnosis can be aided by pain referral patterns, historical features, physical examination maneuvers, and imaging.. Diagnosis can be aided by pain referral patterns, historical features, physical examination maneuvers, and imaging. This pain may worsen with prolonged sitting or standing and can resemble symptoms of sciatica. Web proposed criteria for diagnosis of sacroiliac joint dysfunction can include pain in the area of the sacroiliac joint, reproducible pain with provocative maneuvers, and pain relief with a local. Web eighteen patterns of pain referral were observed. Sacroiliac joint syndrome is a significant source of pain in 15% to 30% of people with mechanical low back pain. Specific pain referral zones reported include the posterior superior iliac spine (psis), 1. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction is a common cause of low back pain and accurate diagnosis can be challenging.. Web eighteen patterns of pain referral were observed. Pain referral from the sacroiliac joint does not appear to be limited to the lumbar region and buttock. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. It can cause sharp, stabbing pain that starts in the hips and pelvis and radiates into the lower back and down the thighs. Sacroiliac joint syndrome. Symptoms that suggest that the sacroiliac joint (sij), as opposed to pathology of the lumbar spine or hip, may be a source of pain include pain with position changes, such as standing from a seated position or sitting on a hard surface. It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. The constellation of symptoms attributed to sijs includes pain referral. A complete history and physical examination are critical in differentiating other. Accurate diagnosis of sacroiliac joint (sij) pain is challenging. The constellation of symptoms attributed to sijs includes pain referral to numerous anatomic regions. Web localized pain is not always a reliable presentation, as a 2000 study reported 18 different pain referral patterns from the si joint. Web the variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying locations of injury with the sacroiliac joint. Quality reporting programs, including the hospital inpatient quality reporting program; Health and safety standards for obstetrical services in hospitals and critical access hospitals; Web to determine the pain referral pattern of the sacroiliac joint in asymptomatic individuals. X the sacroiliac joint is a source of pain. X fortin et al.1 established pain patterns for the sacroiliac joint: Sacroiliac joint syndrome is a significant source of pain in 15% to 30% of people with mechanical low back pain. Pain is the main symptom of si joint dysfunction. Web x sacroiliac joints are the joints of the pelvis where the sacrum connects to the ilium. O typically causes buttock pain but can radiate diffusely down the posterior thigh o does not/rarely cause midline lumbar pain. Identify the etiology of sacroiliac joint injury medical conditions and emergencies. Among these other patterns included pain down the posterior/lateral thigh (50%), pain distal to the knee (28%), and pain in the foot (14%) [14].Sacroiliac Joint Referred Pain
Typical Pain Referral Pattern Of Sacroiliac Joint Pai vrogue.co
Sacroiliac Joint Pain Pontchartrain Orthodepics & Sports Medicine
Sacroiliac Joint Pain "Other Hip Pain" Cornell Pain Clinic
The Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) Beth Forrest Osteopathy
Pain referral from the sacroiliac joint. Van der Wurff et al., 2006 [33
Typical pain referral pattern of sacroiliac joint pain (illustration
SACROILIAC JOINT BIOMECHANICS AND ITS POTENTIAL CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
Si Joint Pain Referral Patterns
The Referral Patterns of the Sacroiliac Joint, Facet Joints, and
Radiation To The Groin Or Fortin Area Also Suggest Sacroiliac Joint As A Source.
Web Eighteen Patterns Of Pain Referral Were Observed.
Outline The Management Options Available For Sacroiliac Joint Injury.
Diagnosis Is Made Clinically With Pain Just Inferior To The Posterior Superior Iliac Spine That Is Made Worse With.
Related Post: