Scm Referral Pattern
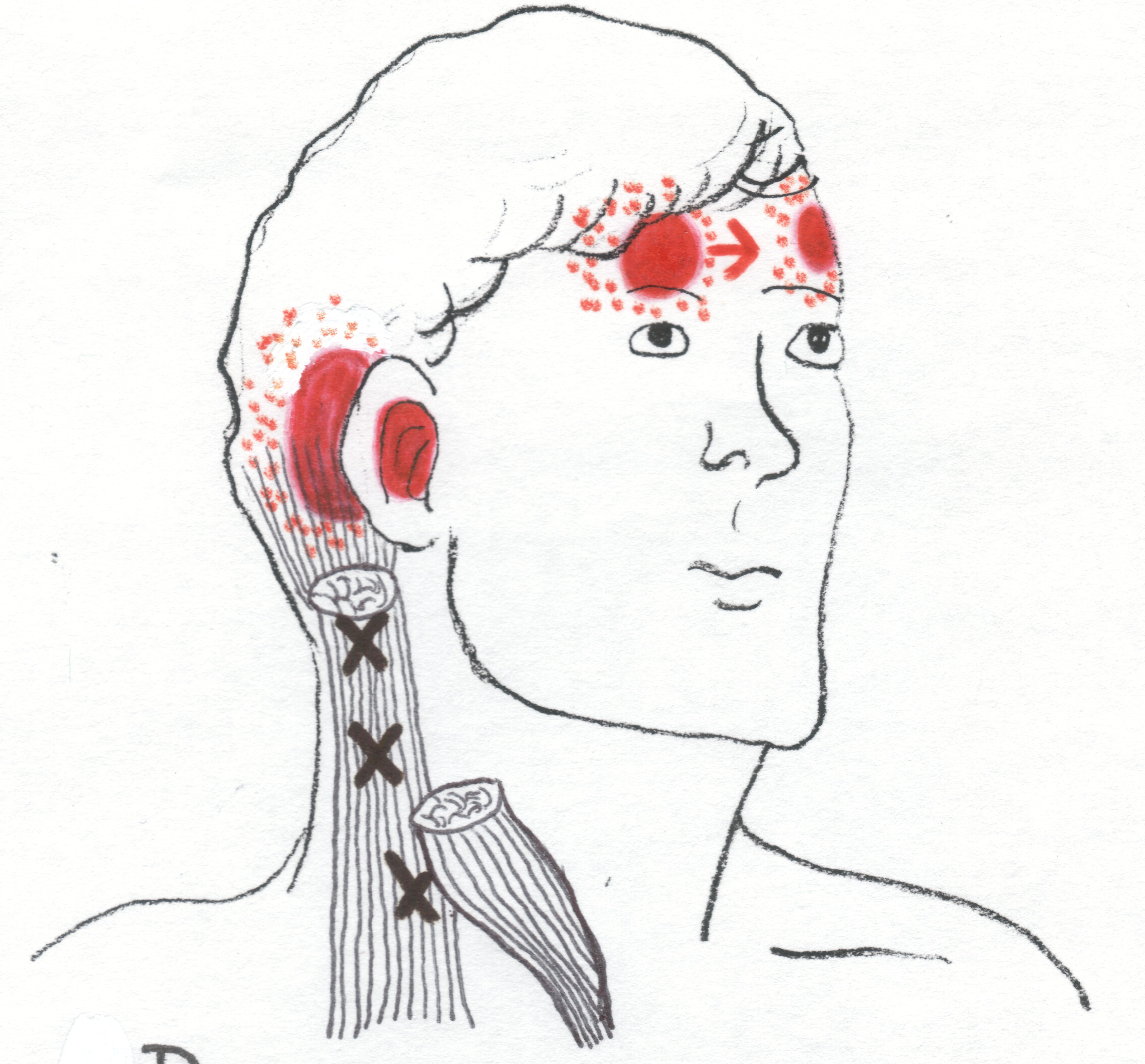
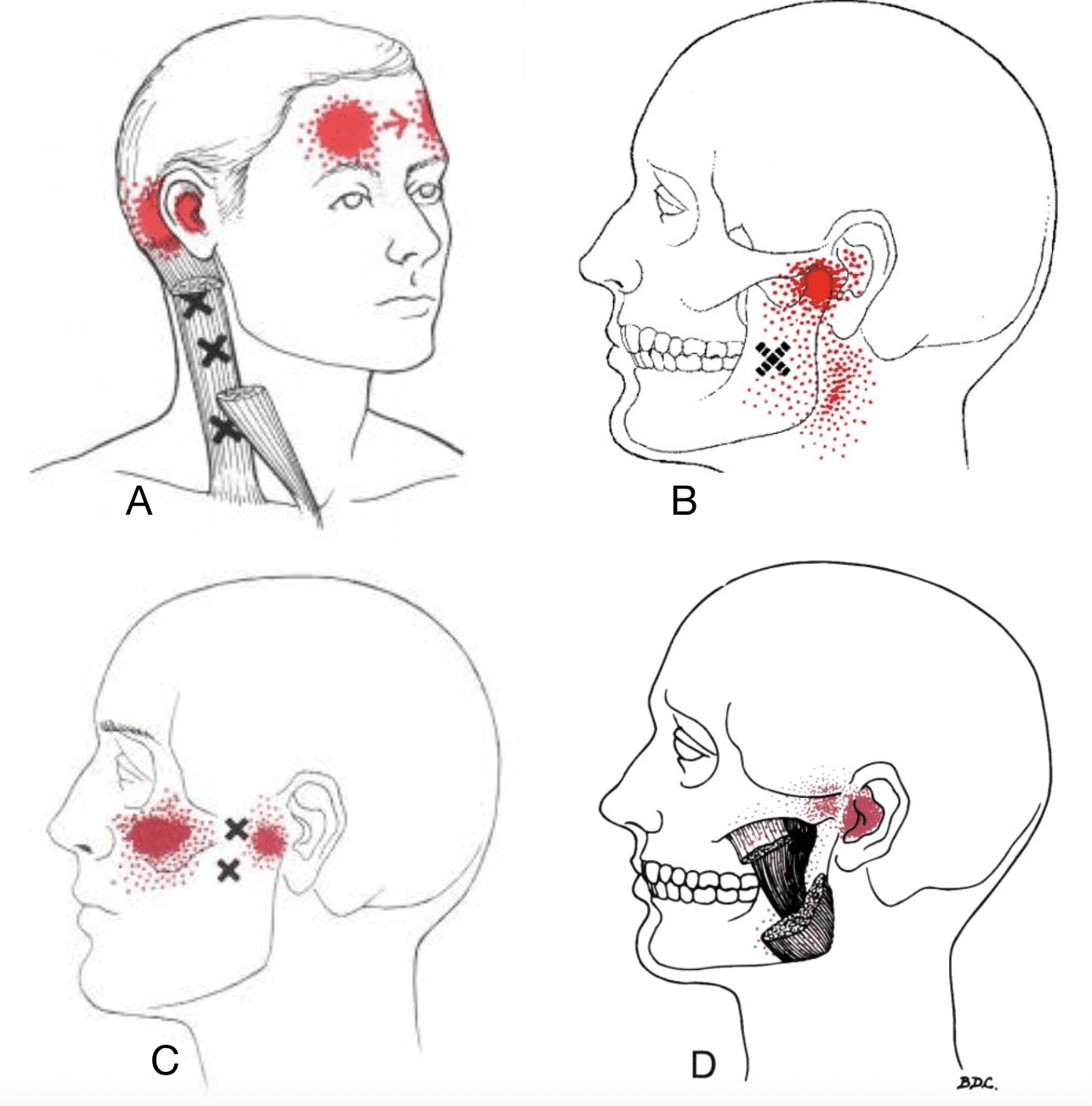
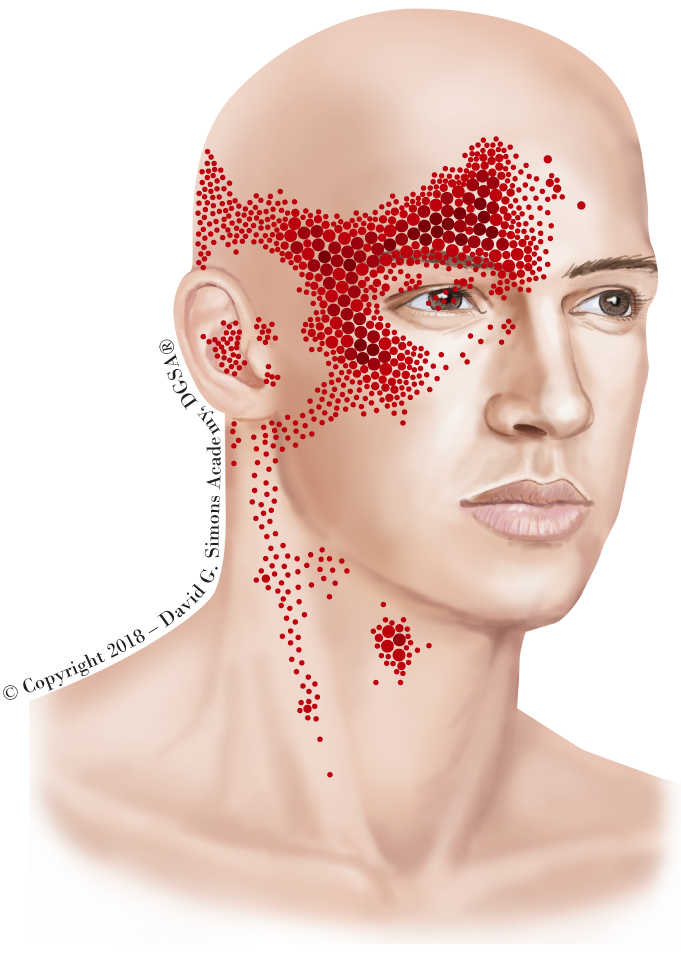
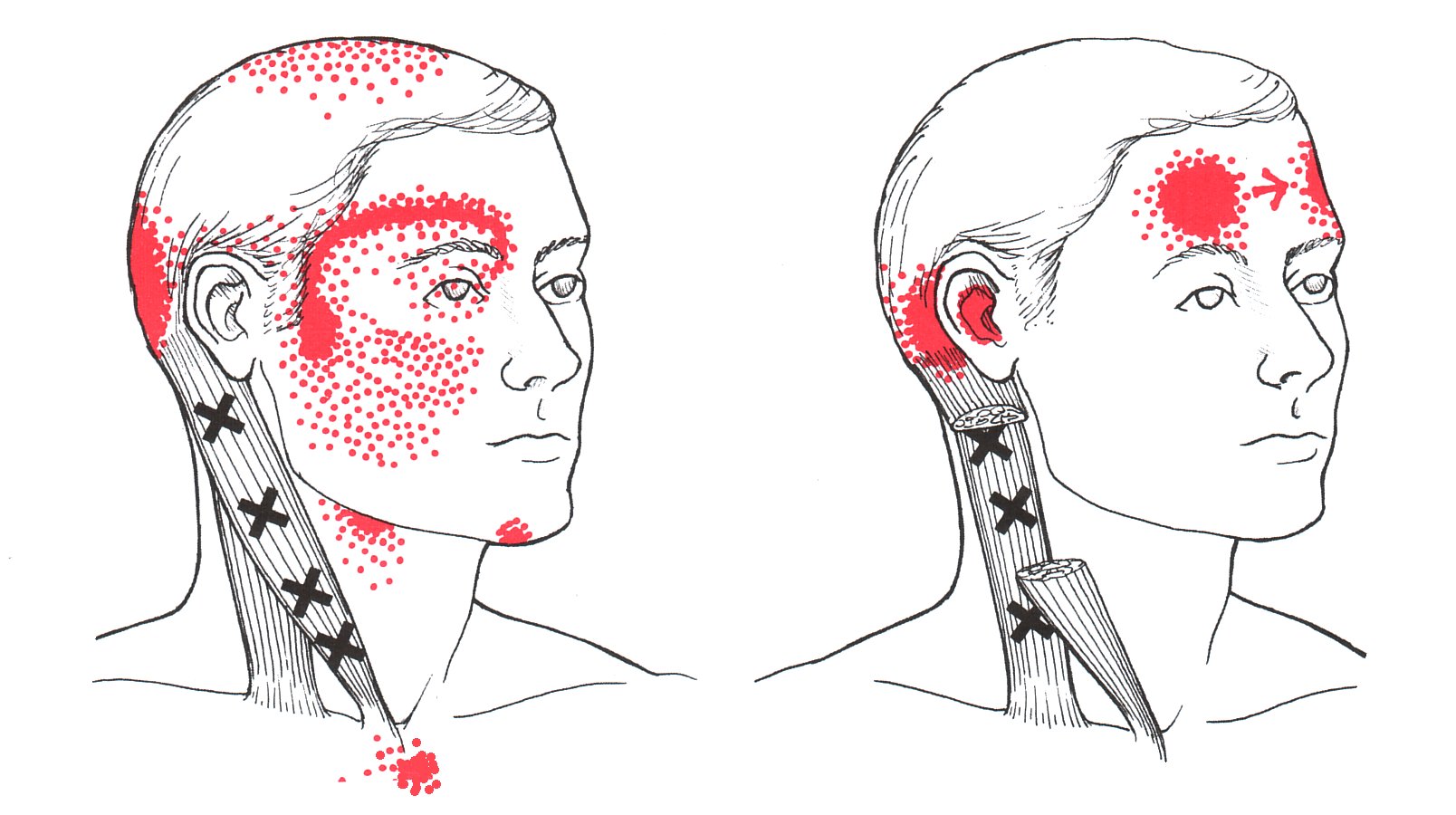
Scm Referral Pattern - This muscle binds the skull to the sternum and clavicle. Web each head of the scm, the clavicular and sternal, can have its own trigger points and so each must be treated separately, but each tend to refer pain upwards to the head, face, and jaws. Conservative management of cervical spine syndromes. Scm trigger points and referred pain. 4 trigger points can be classified as active or latent, with the former causing constant pain and the latter “silent” until aggravated. These altered patterns exist alongside recognised postural changes, including: Web the referred pain is often described as deep and dull. This means that even though the issue is within the scm, the pain is felt in other areas. It can also occur with certain health conditions, such as asthma and. Treatments include stretching, physical therapy and osteopathic manipulation. 4 trigger points can be classified as active or latent, with the former causing constant pain and the latter “silent” until aggravated. Web trigger points are discrete, focal, hyperirritable spots located in a taut band of skeletal muscle. There are 3 in the posterior belly and 4 in the anterior belly. Web trigger points in the sternocleidomastoid (scm) muscle can be a hidden culprit behind persistent neck pain and discomfort. Jaw pain or aching in the cheek areas Web each scm division has a separate and distinct referred pain pattern: Web the upper crossed syndrome refers to a specific pattern of muscle activation (particularly in the neck, trunk, and scapular muscles) with altered movement (i.e. Web a,b the solid red shows the most common referred pain pattern from trigger points (marked with xs) located in the sternal and clavicular divisions of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Web sternocleidomastoid (scm) muscle pain in the neck typically results from muscle tension or performing repeated motions. How does sternocleidomastoid syndrome relate to nerves in the neck? This muscle binds the skull to the sternum and clavicle. Web some of the more common areas that pain is referred from the scm include the sinuses, jaw, temple, eye, and even sometimes, the face. If a patient complains of frontal headaches and the referral has more of a yangming distribution, then i would likely consider yangming points and specifically. Conservative management of cervical spine syndromes. The good thing about having trigger points in your sternocleidomastoids is that you can treat them yourself. [2] it protects the vertical neurovascular bundle of neck, branches of cervical plexus, deep cervical lymph nodes and soft tissues of neck from damage [2] This means that even though the issue is within the scm, the. This muscle binds the skull to the sternum and clavicle. [2] it protects the vertical neurovascular bundle of neck, branches of cervical plexus, deep cervical lymph nodes and soft tissues of neck from damage [2] There are 3 in the posterior belly and 4 in the anterior belly. Web the sternal head of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which is abbreviated as. [2] it protects the vertical neurovascular bundle of neck, branches of cervical plexus, deep cervical lymph nodes and soft tissues of neck from damage [2] Web sternocleidomastoid (scm) muscle pain in the neck typically results from muscle tension or performing repeated motions. If a patient complains of frontal headaches and the referral has more of a yangming distribution, then i. Web each scm division has a separate and distinct referred pain pattern: Compressing the trigger point will commonly elicit a consistent referral pain pattern. Web trigger points are discrete, focal, hyperirritable spots located in a taut band of skeletal muscle. Web the upper crossed syndrome refers to a specific pattern of muscle activation (particularly in the neck, trunk, and scapular. Injuries and tension within your scm can lead to pain and stiffness. Web the upper crossed syndrome refers to a specific pattern of muscle activation (particularly in the neck, trunk, and scapular muscles) with altered movement (i.e. To do this, you need to grab the neck muscles. Does cci play a role in sternocleidomastoid syndrome? The good thing about having. Web referred pain pattern of trigger points in the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Web the upper crossed syndrome refers to a specific pattern of muscle activation (particularly in the neck, trunk, and scapular muscles) with altered movement (i.e. Web common pain referral patterns for muscles of the head and neck which can produce orofacial pain have been described extensively. The red areas. From a cervicogenic pain perspective, the upper trape‐zius muscle is a major source of referral and can refer pain to the angle and lower border of the mandible, and into the temporal and suboccipital region. Web sternocleidomastoid (scm) muscle pain in the neck typically results from muscle tension or performing repeated motions. This muscle binds the skull to the sternum. This means that even though the issue is within the scm, the pain is felt in other areas. It can also occur with certain health conditions, such as asthma and. Scm trigger points and referred pain. Web each scm division has a separate and distinct referred pain pattern: This muscle binds the skull to the sternum and clavicle. Web common pain referral patterns for muscles of the head and neck which can produce orofacial pain have been described extensively. Web each head of the scm, the clavicular and sternal, can have its own trigger points and so each must be treated separately, but each tend to refer pain upwards to the head, face, and jaws. 4 trigger points. Web trigger points in the sternocleidomastoid (scm) muscle can be a hidden culprit behind persistent neck pain and discomfort. It can refer pain in front of the ear. Web referred pain pattern from sternocleidomastoid trigger points. You can care for your scm by managing stress and. This muscle binds the skull to the sternum and clavicle. Conservative management of cervical spine syndromes. Web if you review the trigger point (trp) referral patterns of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, you will see that it refers pain to a number of regions. Web referred pain pattern of trigger points in the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Scm trigger points and referred pain. How does sternocleidomastoid syndrome relate to nerves in the neck? Does cci play a role in sternocleidomastoid syndrome? There are 3 in the posterior belly and 4 in the anterior belly. Web some of the more common areas that pain is referred from the scm include the sinuses, jaw, temple, eye, and even sometimes, the face. In the sternal head of scm, there are usually 4 tps which can give issues as ptosis, blurred vision, sinus headaches and referred pain pattern. Trigger points are classified as being active or latent. Injuries and tension within your scm can lead to pain and stiffness.Scalene Trigger Point Referral Pattern Trigger points, Dry needling
Figure 1 Referred pain patterns from upper trapezius
SCM & TMJ Referral Pattern Massage Tips, Massage Techniques, Massage
Sternocleidomastoid SCM © Copyright American Academy of Manual Medicine
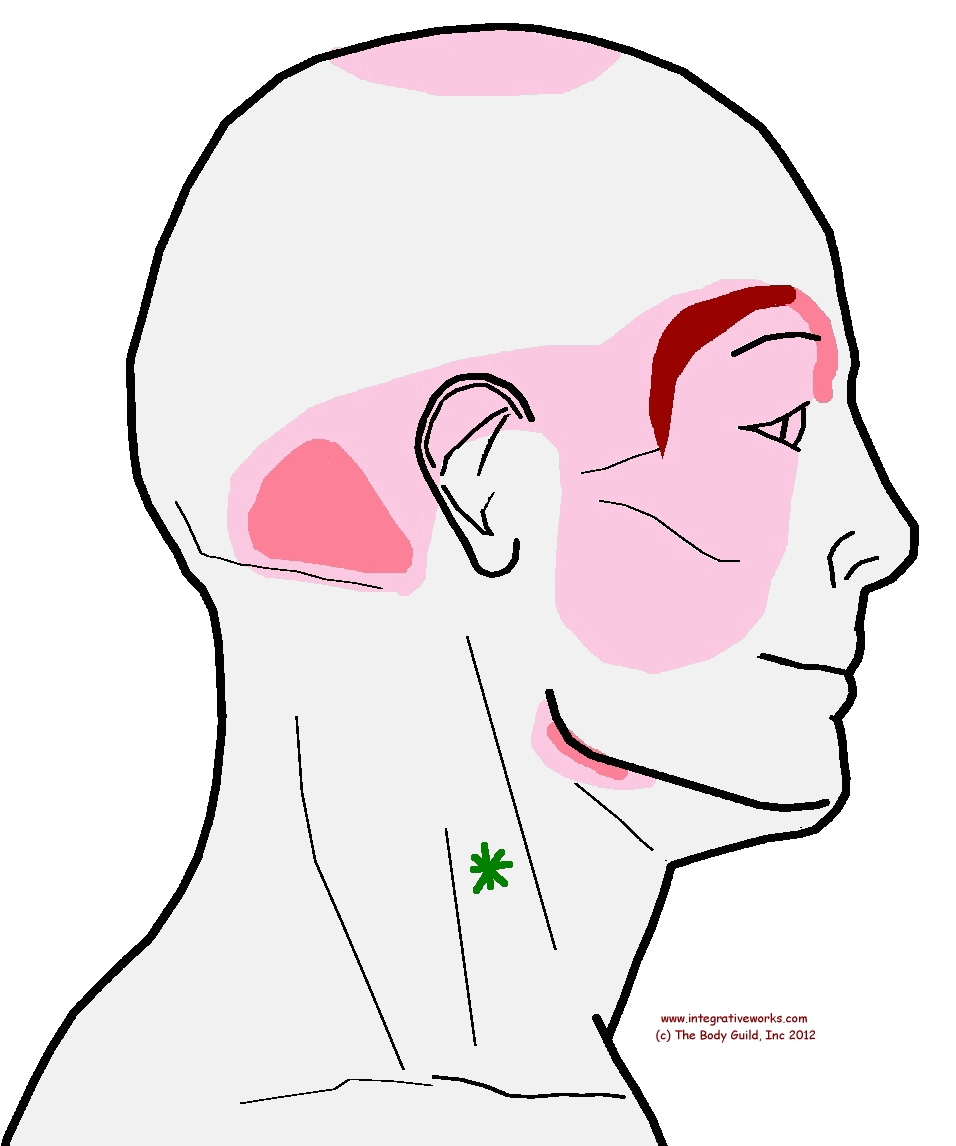
referral SCM sternal Integrative Works
Your Frustrating Ear Pressure May Actually Be Your TMJ The Jaw Therapist
Myofascial Trigger Points we have been studying them since 1995 David
Scm Trigger Points
A,B The solid red shows the most common referred pain pattern from
Sternocleidomastoid The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide
Web What Is Sternocleidomastoid Syndrome?
Web Common Pain Referral Patterns For Muscles Of The Head And Neck Which Can Produce Orofacial Pain Have Been Described Extensively.
Trigger Point Therapy Techniques, Such As Manual Pressure Or Massage, Can Be Effective In Releasing Tension And Alleviating Pain Associated With Trigger Points In The Scm Muscle.
4 Trigger Points Can Be Classified As Active Or Latent, With The Former Causing Constant Pain And The Latter “Silent” Until Aggravated.
Related Post: